Inductive conductivity sensors in the chlor-alkali industry
In the chlor-alkali industry, online pH and ORP analyzers have been widely used in production processes such as brine refining, membrane denitrification, electrolytic cells, and light brine dechlorination, helping companies improve the purity of brine, promote production efficiency, and extend the service life of equipment. Today, another online analysis technology, inductive conductivity, is increasingly used in chlor-alkali production sections, such as sodium hypochlorite production to monitor caustic soda residual concentration, chlorine drying to detect changes in concentrated sulfuric acid concentration, and hydrochloric acid synthesis to detect hydrochloric acid concentration.
So how do inductive conductivity sensors play a role in sodium hypochlorite production and chlorine drying processes? What is the basic principle of inductive conductivity measurement?
Sodium hypochlorite production monitors caustic soda residual concentration
Chlorine gas enters the lower part of the chlorine absorption tower and is absorbed by countercurrent contact with the circulating cooling alkali liquid sprayed on the upper part of the tower. A chemical reaction occurs in the absorber part to generate sodium hypochlorite.
The absorption alkali liquid flows out from the bottom of the tower to the absorption alkali liquid low-level tank, and then is transported to the absorption alkali cooler through the absorption alkali circulation pump for cooling, and then returns to the top of the tower for the next round of absorption. The reaction process is as follows:
2NaOH + Cl₂ => NaOCl + NaCl + H₂O
In this process, it is necessary to understand the absorption capacity of caustic soda, residual caustic soda content and sodium hypochlorite concentration. Conductivity measurements reflect the total ion concentration of the caustic soda absorption solution and by-products.
As the caustic soda solution is consumed, the conductivity value usually decreases. At the same time, as the concentration of conductive products increases, the decrease in conductivity slows down. However, caustic soda conducts electricity more strongly than inorganic salt products, so as the chemical reaction continues, a continuous decrease in conductivity values can be observed.
At a certain concentration, the caustic soda solution begins to lose its ability to absorb chlorine gas. Conductivity measurement can determine this value, and then start discharging the absorbent solution while adding fresh solution. The residual caustic soda concentration can also be calculated through conductivity.
This point is usually measured in conjunction with the ORP parameter. An increase in the ORP value means an increase in the sodium hypochlorite concentration. If it is continuous production, only ORP measurement is often used to control it within a stable ORP range to ensure product concentration.
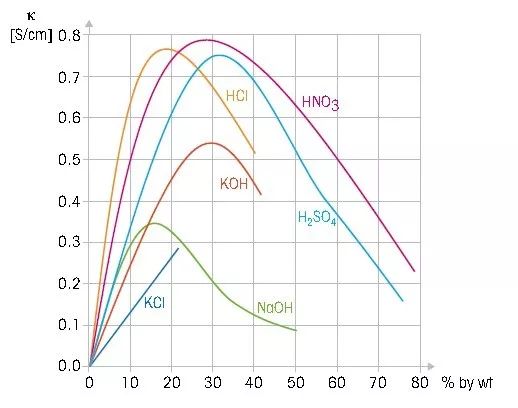
Corresponding relationship between conductivity and acid-base concentration
Chlorine drying to detect concentrated sulfuric acid concentration
The chlorine gas produced by electrolysis contains a large amount of water vapor, which has a strong corrosive effect on subsequent transmission pipelines and compressors. Therefore, cooling measures need to be taken to reduce the partial pressure of saturated water vapor and reduce the water content in chlorine gas.
Then the chlorine gas enters the bottom of the packed tower, and passes through the packing layer and the 98% sulfuric acid sprayed from the top of the tower from bottom to top. The sulfuric acid fully contacts the chlorine gas and absorbs the remaining moisture. If the sulfuric acid concentration drops to 75%, pump it to the dilute sulfuric acid storage. groove.
Changes in sulfuric acid concentration must be monitored in this section. Otherwise, when the sulfuric acid concentration drops to 75%, it will no longer have the ability to absorb moisture, resulting in poor drying effects and corrosion of expensive compressors and pipelines.
At this time, Aumeascon’s inductive conductivity analyzer can be used to monitor changes in sulfuric acid concentration. The corresponding curve between sulfuric acid concentration and conductivity is three segmented curves, such as H2SO4-1 (0-30 %), H2SO4-2 (32-84 %), H2SO4-3 (92-99 %), which need to be transmitted Select the corresponding concentration curve in the instrument, however most instruments can only select one curve.
During the chlorine drying process, the change range of sulfuric acid concentration spans the H2SO4-2 (32-84 %), H2SO4-3 (92-99 %) curves, and the transmitter cannot automatically switch curves. You can use a transmitter that can set two curves at the same time and has two analog outputs. The control system automatically selects the appropriate measurement curve based on the changes in the two analog signal outputs.
Aumeascon’s Solution
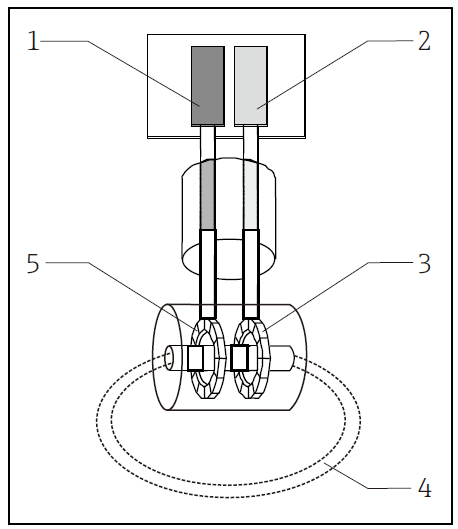
The inductive conductivity sensor consists of two toroidal coils encased in a chemically resistant polymer housing without any exposed metal. After the sensor is placed in a conductive solution, a current loop is generated, and the current value is proportional to the conductivity of the solution. AM-D-ICS PFA material inductive conductivity sensor is not afraid of dirt and is ideal for highly conductive solutions! Made of chemically resistant PFA, it completely eliminates sensor corrosion problems!